The Agile Scale-Up: A Blueprint for SMO Growth Using Embedded Teams
15 Sept, 202510 minsSite Management Organizations (SMOs) are entering a decisive decade. The historical model of...

Site Management Organizations (SMOs) are entering a decisive decade. The historical model of linear, permanent hiring is no longer sufficient to navigate the complexities of modern clinical development. Sponsors demand unprecedented speed delivering high quality data, and deep therapeutic area (TA) specialization across multiples regions. With the prevailing economic headwinds, operational agility has become a primary determinant of survival as well as market leadership. SMOs that successfully scale will be those that master a dynamic, flexible approach to talent and operations, preserving capital while accelerating growth.
This white paper presents a practical blueprint for scaling an SMO through employing a blended staffing architecture comprised of fractional, embedded, and permanent talent. We will demonstrate that the optimal mix of these staffing models is not static but must evolve in concert with an organization’s journey through three distinct phases: Start-up & Expansion, Growth, and Maturity. The traditional challenge of balancing fixed overhead against fluctuating project demand can be solved by embracing a variable cost structure, with embedded teams serving as the engine for rapid, consistent, and compliant expansion.
Our analysis reveals that one size does not fit all. Early-stage SMOs should prioritize flexibility, aiming for an 80/20 split of flexible-to-permanent staff to de-risk operations and conserve capital. As an SMO enters its growth phase, the model should shift to a 70/30 balance, building organizational depth and converting top performers to anchor institutional knowledge. At maturity, this 70/30 ratio is strategically maintained to drive optimization, retain institutional expertise, and defend against market complacency.
Additional findings from our analysis:
• Embedded teams are your scaling engine. They drive speed-to-scale, process consistency, compliance, and sponsor confidence while reducing fixed overhead.
• Permanent roles are your core. They anchor institutional knowledge, governance, and leadership. Transition top-performing embedded and fractional talent to permanent roles selectively as you grow.
• Technology enablement is a strategic multiplier. Finance automation, system interoperability, and centralized data management unlock productivity and readiness for AI/ML, real-world evidence integration, and multi-region operations.
• De-risk with a structured and thoughtful human capital strategy. Assess your current state, stand up tailored staffing models and systems, then operate and optimize with data-driven oversight.
This blueprint is operationalized through the Strategic Solutions Group’s (SSG) phased Advise-Build-Operate (ABO) approach that provides a de-risked pathway for SMOs to assess their current capabilities, design and build a bespoke operating model, and implement a system of continuous, data-driven performance optimization. By bridging the critical gap between strategy and execution, this framework enables SMO leaders to extend their cash runway, accelerate site activation, and build a resilient, technology-enabled organization poised for sustained, profitable growth.
The Strategic Imperative: Redefining the SMO Operating Model
The pressure on pharmaceutical and life science sponsors to bring novel therapies to market faster and more efficiently is being directly transferred to their network of clinical research partners. For Site Management Organizations, this pressure manifests as a complex set of competing demands: deliver flawless execution on increasingly complex protocols, ensure robust patient recruitment and engagement, maintain compliance across multiple regulatory jurisdictions, all while driving efficiencies to ensure margins.
The legacy approach to scaling an SMO—hiring permanent, full-time staff in direct proportion to anticipated new site openings or trial awards—is proving increasingly fragile. This model exposes organizations to significant financial risk. The fixed costs associated with salaries, benefits, and overhead become a heavy burden during the inevitable lulls between studies or in the face of unexpected trial delays. Conversely, during periods of rapid growth, the traditional hiring process is often too slow to meet sponsor timelines, resulting in missed opportunities and potential damage to the SMO’s reputation for reliability.
The modern SMO must therefore operate as an agile, adaptable entity. The central strategic challenge is no longer simply how to grow, but how to build for growth. This requires a fundamental rethinking of the organization’s human capital structure. The solution lies in moving away from a monolithic workforce and toward a blended, fit-for-purpose model that combines the stability of a core permanent team with the flexibility and specialized expertise of fractional and embedded resources. This strategic blend of talent provides the operational leverage needed to scale up capacity in response to demand and scale down costs during quieter periods, creating a more resilient and financially sound enterprise.
Today, leading SMOs are distinguished not just by the number of sites they manage, but by their demonstrated leadership in specific therapeutic areas, their adoption of technology to drive efficiency, and their ability to integrate and analyze data to provide deeper insights. A flexible staffing model is an enabler of this differentiation, allowing an SMO to rapidly onboard niche TA experts or data scientists for specific projects without the long-term commitment of a permanent hire.
In this context, an SMO’s staffing strategy becomes its corporate strategy. The ability to design and deploy the right mix of talent at the right time is the most critical lever for de-risking growth, extending the cash runway, and ultimately, accelerating the journey to market leadership.
The Three Stages of SMO Growth: A Stage-Gated Staffing Architecture
An SMO’s operational needs, strategic priorities, and risk tolerance change dramatically as it scales. A one-size-fits-all staffing model is therefore destined to fail. A sophisticated scaling strategy aligns the composition of the workforce with the specific demands of the organization’s current stage of development. We have identified three distinct stages in the SMO lifecycle: Start-up & Expansion, Growth, and Maturity. Each stage has a unique set of objectives that dictates a corresponding optimal staffing mix.
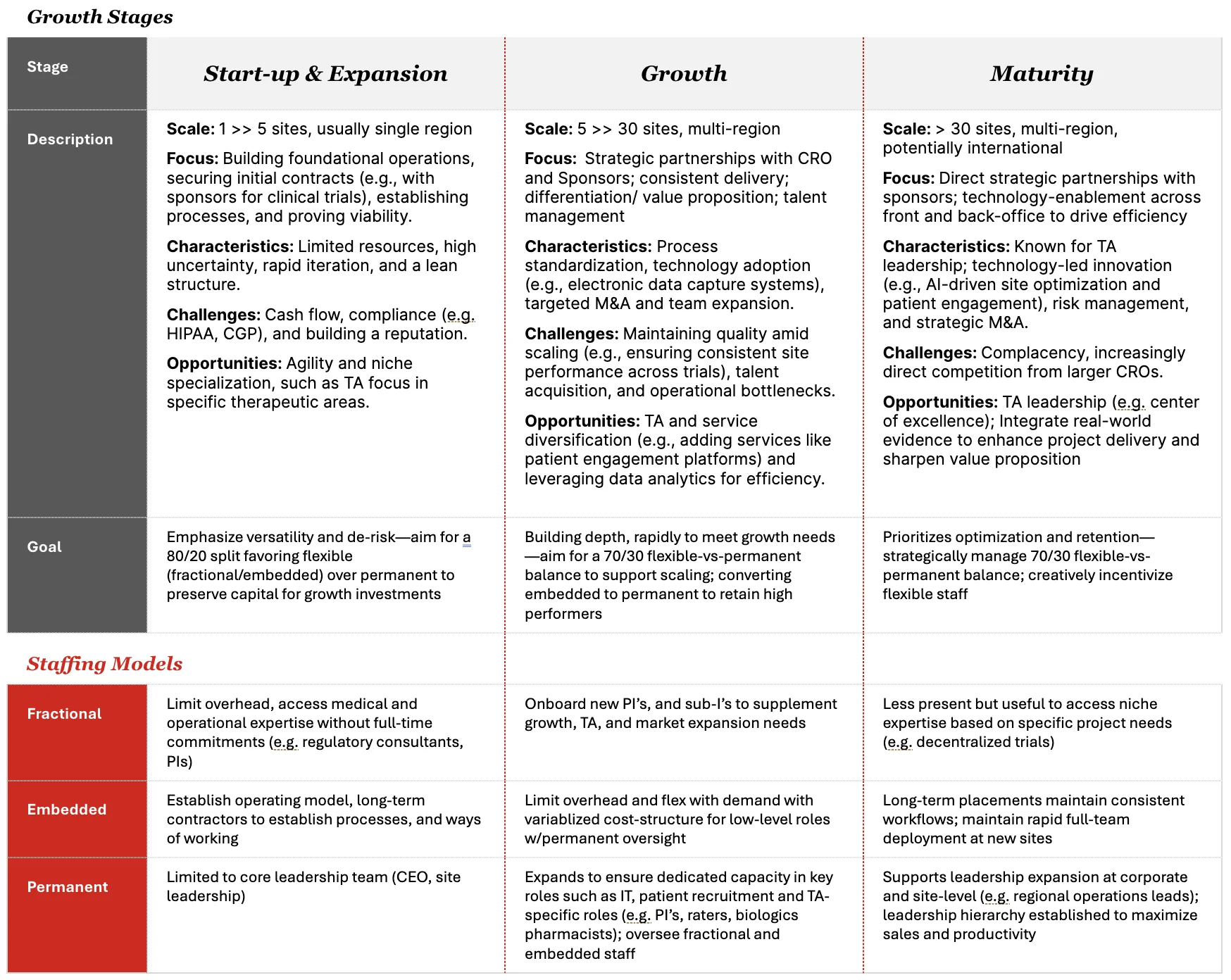
Stage 1: Start-up & Expansion (1 to 5 sites)
During this initial phase, the SMO’s primary focus is on establishing its foundational operations and proving its viability. The organization is typically lean, resource-constrained, and operating in a single region. The core objectives are to secure initial contracts with sponsors, establish robust and compliant processes, and begin building a reputation for reliable delivery. The operating environment is characterized by high uncertainty and rapid iteration. The most significant challenges are managing cash flow, ensuring strict adherence to regulations like HIPAA and GCP, and overcoming the initial hurdle of being an unknown entity in the market.
The strategic staffing goal in this stage is to maximize versatility and de-risk the venture by preserving capital. We recommend a staffing composition that heavily favors flexible talent, targeting an 80/20 split between flexible (fractional/embedded) and permanent staff. A small, core permanent team, typically comprising the CEO and key site leadership, provides the strategic direction and essential oversight. This lean leadership structure is then augmented with a suite of flexible resources.
Fractional experts are invaluable at this stage. They provide access to critical medical and operational expertise without the financial burden of full-time salaries. For example, a fractional regulatory consultant can guide the development of compliant SOPs, a fractional business development professional can help secure the first crucial contracts, and part-time Principal Investigators (PIs) can be brought on to establish a presence in a new therapeutic area.
Embedded contractors are used to establish the core operating model. These long-term, project-based resources, such as Clinical Research Coordinators (CRCs) and data managers, are tasked with creating the initial processes and ways of working. They provide the necessary manpower to execute the first trials while maintaining a variable cost structure that flexes with project demand. This approach allows the SMO to build a track record without committing to a large, permanent payroll, thereby extending its financial runway for crucial growth investments.
Stage 2: Growth (5 to 30 sites)
Having proven its model, the SMO now enters a phase of rapid expansion, often moving into multiple regions. The strategic focus shifts from mere viability to achieving consistent delivery at scale. This involves forging strategic partnerships with CROs and sponsors, clearly articulating a differentiated value proposition, and implementing a robust talent management strategy. Key activities include standardizing processes across all sites, adopting new technologies to enhance the patient experience, and potentially pursuing targeted M&A to accelerate expansion.
The primary challenges in the growth phase are maintaining quality and consistency as the organization scales, overcoming operational bottlenecks, and winning the war for top talent. The opportunities, however, are significant. The SMO can begin to diversify its service offerings, Tas/indications and can start to leverage data analytics to drive operational efficiency.
The staffing goal during this phase is to build organizational depth rapidly to meet the demands of growth. The recommended staffing balance shifts to a 70/30 flexible-to-permanent ratio. This reflects the need to build a more robust internal infrastructure while still retaining significant operational flexibility. A key activity during this stage is the selective conversion of high-performing embedded contractors into permanent employees, thereby retaining valuable institutional knowledge and leadership potential.
The permanent team expands to ensure dedicated capacity in key functional areas. Roles such as IT leadership, heads of patient recruitment, and TA-specific leaders become permanent fixtures. These individuals provide the necessary oversight for the growing contingent of fractional and embedded staff. Fractional experts continue to play a vital role, particularly in onboarding new PIs and Sub-Investigators to support TA and market expansion needs. Embedded teams remain the workhorses of scaling, allowing the SMO to limit overhead and maintain a variabilized cost structure for site-level roles, all under the guidance of permanent operational leaders. This hybrid structure—a permanent core overseeing flexible teams—provides the ideal combination of stability and agility required for this dynamic phase.
Stage 3: Maturity (>30 sites)
At this stage, the SMO is a well-established entity, often with a multi-region or international presence. It is known for its leadership in specific therapeutic areas and is increasingly leveraging technology to drive efficiency across both front-office and back-office functions. The strategic focus shifts toward securing direct, high-value strategic partnerships with sponsors and managing risk. The organization is characterized by its technology-led innovation, such as using AI for site optimization, and its pursuit of strategic M&A to consolidate its market position.
The challenges at maturity can be subtle but significant: organizational complacency and potentially direct competition with CRO as sponsors partner directly. The greatest opportunities lie in cementing TA leadership by establishing Centers of Excellence and integrating real-world evidence (RWE) to enhance project delivery and sharpen the SMO’s value proposition to sponsors.
The staffing goal at maturity is to prioritize optimization and retention. The SMO strategically manages a 70/30 flexible-to-permanent balance, resisting the temptation to bloat its permanent ranks. This discipline ensures that the organization remains agile and cost-efficient. The focus shifts to creatively incentivizing and retaining the high-performing flexible staff who are critical to its success.
The permanent hierarchy is now well-established, supporting leadership expansion at both the corporate and site levels, with roles like regional operations leads maximizing sales and productivity. Embedded teams continue to be a cornerstone of the operating model. Long-term placements ensure consistent workflows and provide the ability to rapidly deploy full teams to new sites or projects. Fractional experts are used more selectively to access highly specialized, niche expertise for specific project needs, such as designing decentralized trials or advising on entry into a new international market. By maintaining a significant portion of its workforce as flexible, the mature SMO retains the agility to pivot quickly in response to market changes, a crucial advantage in fending off larger, more cumbersome competitors.
A Data-Driven View of the Evolving Staffing Model
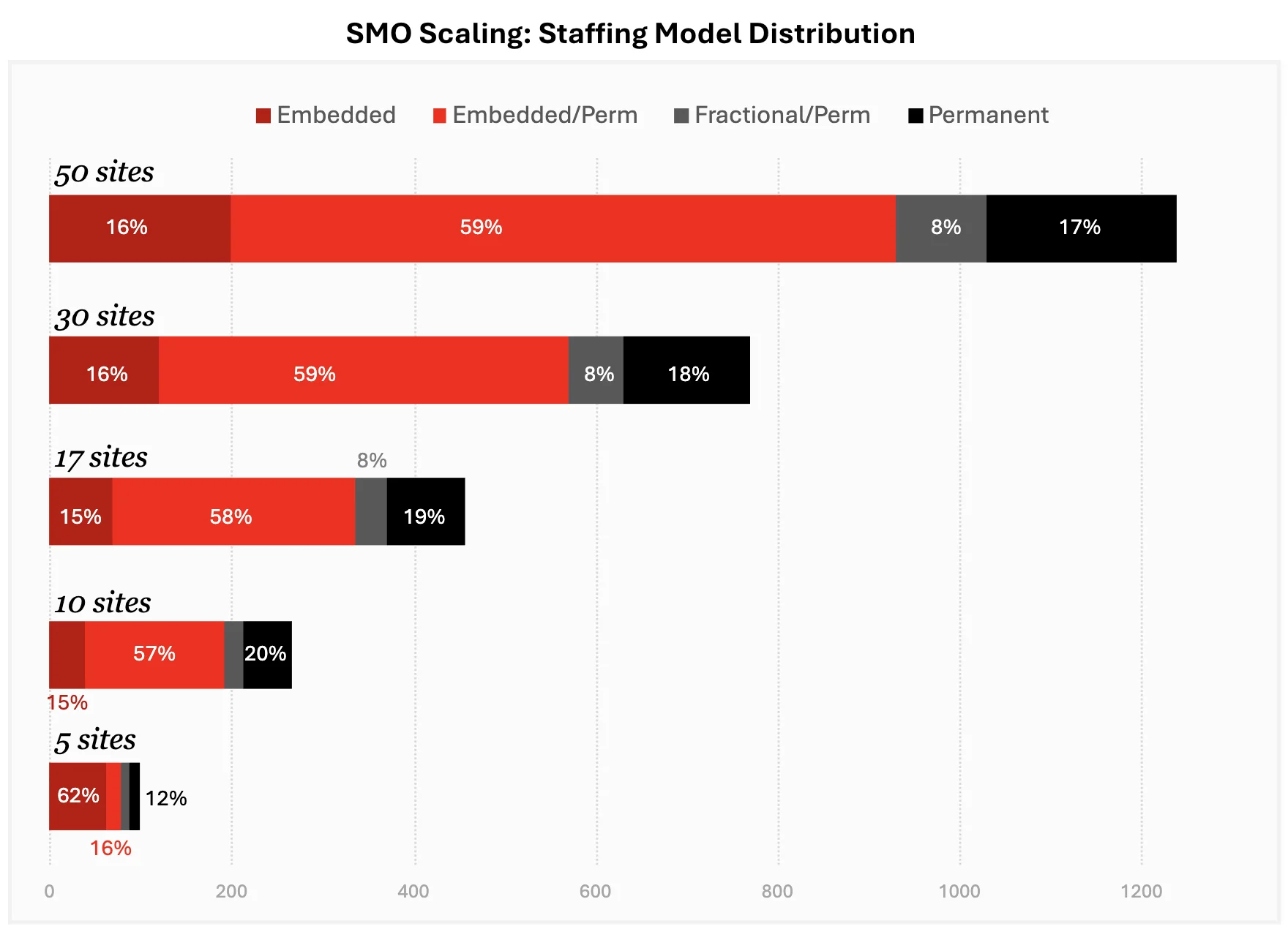 Source: SSG, Barrington James analysis
Source: SSG, Barrington James analysis
The theoretical framework of evolving staffing ratios is borne out by market analysis. By examining the workforce composition of SMOs at different scales, a clear pattern emerges. As an organization grows from a handful of sites to a network of 50 or more, the distribution of fractional, embedded, and permanent roles shifts in a predictable and strategic manner.
As the data illustrates, early-stage SMOs with around five sites rely heavily on embedded and fractional talent. This reflects the capital-preservation and agility imperatives discussed earlier. As the SMO scales to 10 and then 17 sites, the proportion of permanent staff grows, but embedded teams remain the largest single component of the workforce, fueling the expansion. By the time an SMO reaches 30 and then 50 sites, the ratio stabilizes, with a strong permanent leadership and operational core complemented by a majority-flexible workforce. This data validates the principle that scaling is not simply about adding more people; it is about adding the right ‘type’ of people at the right time.
The roles fulfilled by each staffing model are distinct. Fractional roles, typically requiring 5-20 hours per week, are best suited for engaging specialized expertise without a long-term commitment. In the early stages, this includes functions like business development, contracts, IT strategy, and HR setup. Embedded resources, who may be full-time contingents or project-based, are the key to rapid scaling. They provide dedicated, hands-on support that ensures process consistency, faster decision-making, and compliance at the site level. These are roles like CRCs, data managers, and patient recruitment specialists. Finally, permanent employees provide the operational stability, strategic leadership, and institutional knowledge that form the bedrock of the organization. This includes the executive team, regional leadership, site management, and any high-performing "keepers" who are transitioned from flexible roles to become permanent assets.
The journey of an SMO is one of continuous transformation. The staffing model must mirror this journey, embracing flexible teams at the outset and then thoughtfully integrating more permanent and mixed models to support sustained growth and long-term optimization.
Building the Scalable Team: Corporate and Site Composition
As an SMO transitions into the growth phase, typically around the 20-25 site mark, the complexity of its organizational structure increases significantly. Both the corporate headquarters and the individual sites require a carefully architected mix of roles to support multi-region operations, ensure compliance, and drive efficiency. The composition of these teams is not arbitrary; it is a direct reflection of the strategic priorities of a scaling organization.
A key theme for leading SMOs by 2030 will be the automation and integration of back-office functions. Many organizations today are hampered by manual financial compiling and a lack of system interoperability. Forward-thinking leaders are implementing automation platforms and ensuring their various systems can communicate seamlessly to drive significant productivity gains. This technology enablement has a direct impact on team composition, particularly at the corporate level.
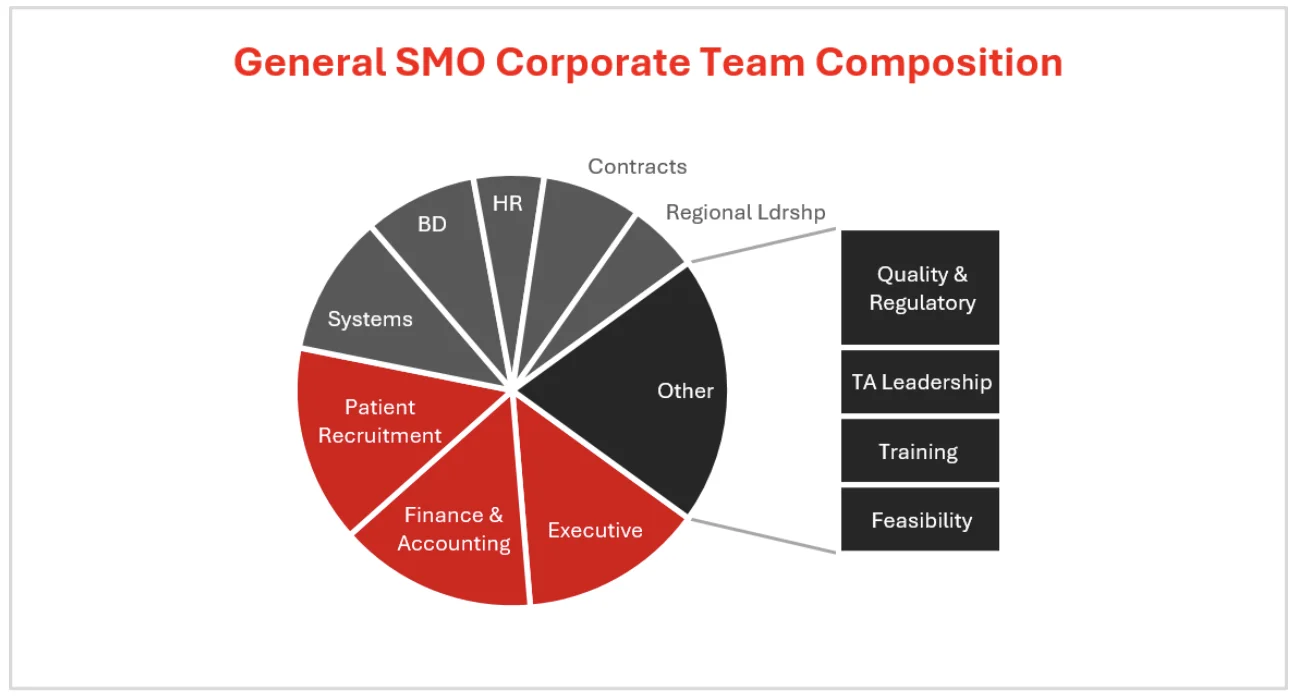
At the corporate level, the team must evolve to support a distributed network of sites. The executive team provides overall strategic direction. Functions like Finance & Accounting become more sophisticated, moving beyond basic bookkeeping to strategic financial planning and analysis. A centralized Patient Recruitment team, augmented by data analytics, works to support local site efforts with broader digital campaigns and predictive modeling. The Systems/IT function becomes critically important, scaling to streamline data flows, enable centralized data management, and lay the groundwork for future AI and machine learning adoption. As the organization expands into new regions, roles such as Regional Leadership and centralized Quality & Regulatory are duplicated to ensure local compliance and harmonize operations. Other key corporate functions include Business Development, HR, Contracts, TA Leadership, Training, and Feasibility.
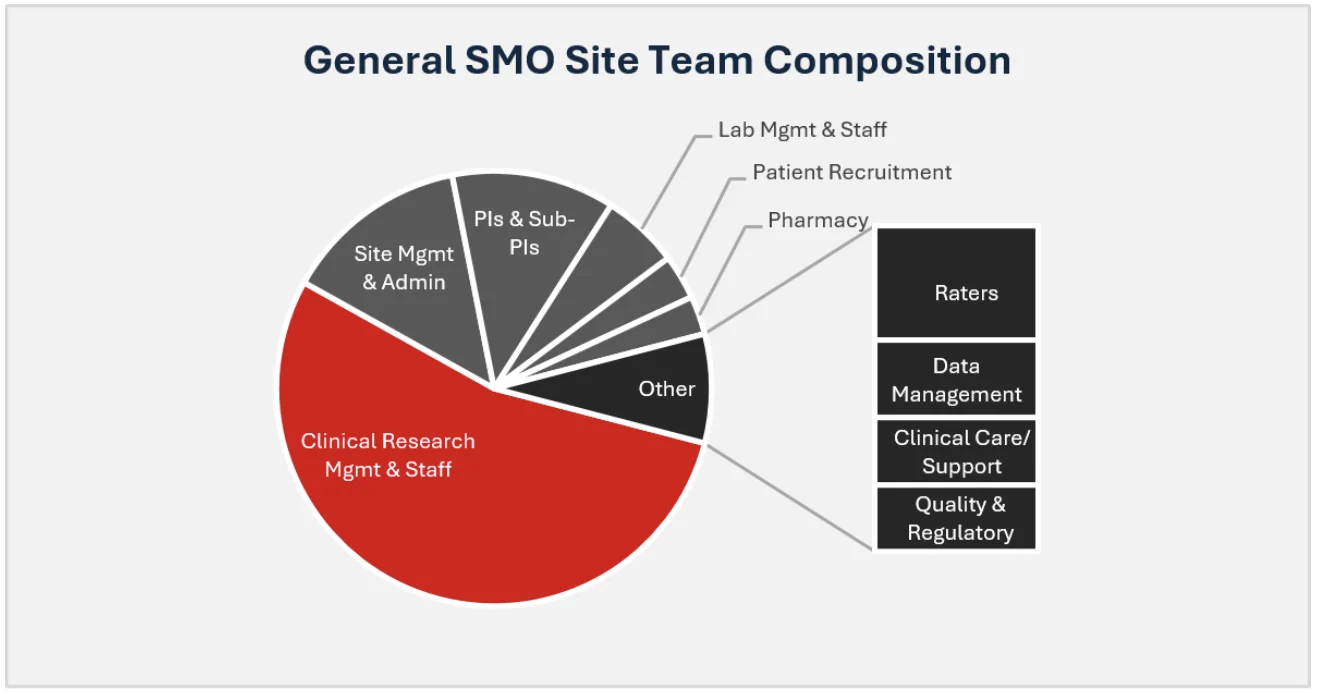
At the site level, the team remains focused on the core activities of clinical trial execution. However, the structure becomes more professionalized and specialized. Site Management & Administration provides the operational backbone. A team of PIs & Sub-PIs, often a mix of permanent and fractional staff, provides the necessary medical oversight and TA expertise.
Clinical Research Management & Staff, primarily composed of embedded CRCs, execute the day-to-day trial activities. This core team is supported by a range of specialized functions. A dedicated Patient Recruitment team works on local outreach. The Pharmacy, Lab Management, and specialized Raters support the specific requirements of the trial protocols. Data Management ensures the integrity of the information collected, while a local Quality & Regulatory function ensures adherence to all relevant standards. This entire site structure is designed for consistency and repeatability, allowing the SMO to deliver a predictable level of quality and performance to sponsors, regardless of the site’s geographic location.
The Path to Execution: SSG’s Advise-Build-Operate (ABO) Model
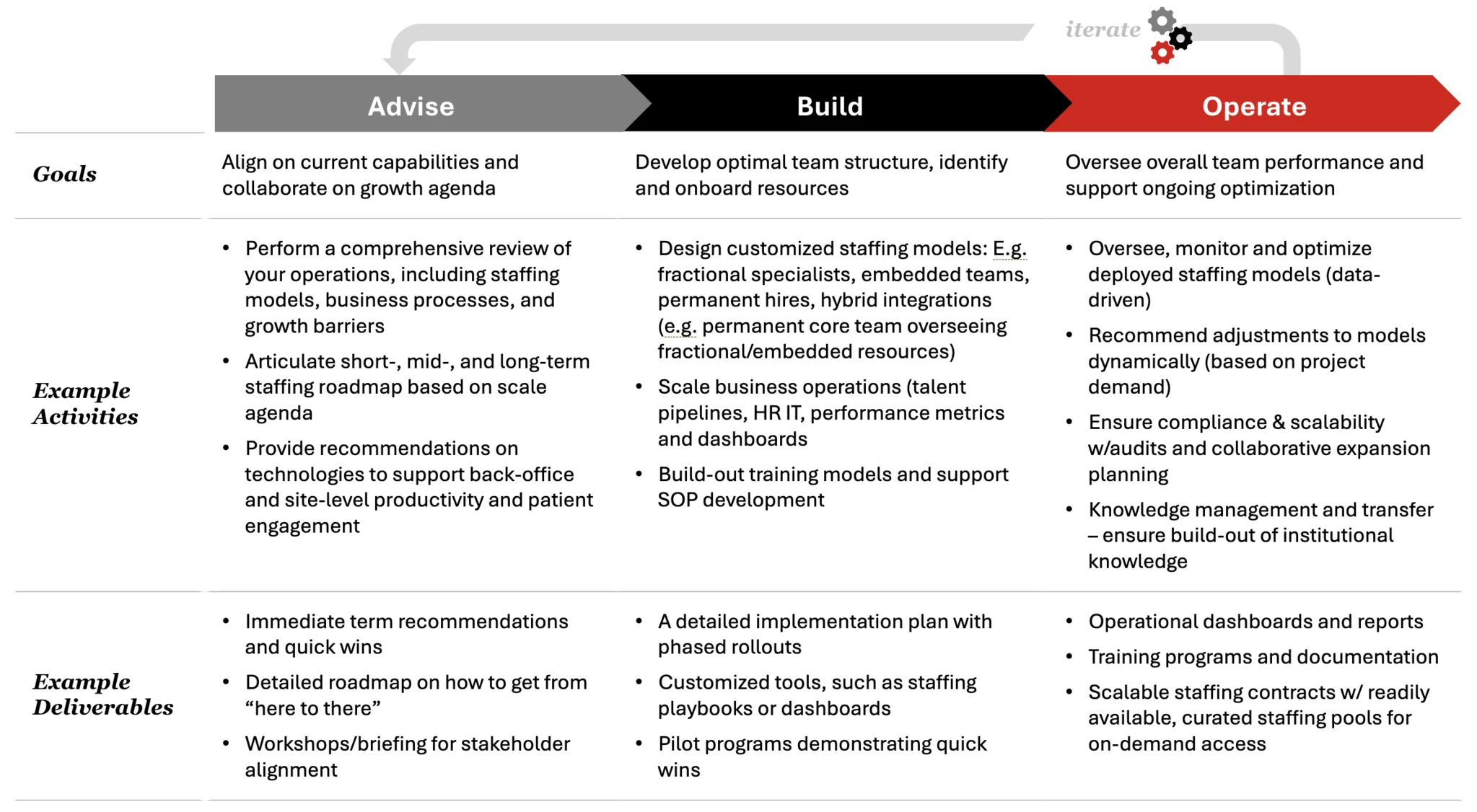
The ABO model is a phased, collaborative engagement that guides an SMO through the entire transformation process.
Phase 1: Advise
The journey begins with a deep, collaborative alignment on the organization’s current state and future ambitions. The goal of the Advise phase is to develop a clear-eyed understanding of existing capabilities and to co-create a pragmatic growth agenda. This involves a comprehensive review of the SMO’s operations, including its current staffing models, business processes, technology stack, and existing growth barriers. We work with leadership to articulate a detailed short-, mid-, and long-term staffing roadmap that is directly tied to the organization’s scale agenda. This phase also includes providing concrete recommendations on technologies that can support both back-office productivity and site-level patient engagement. The key deliverables from this phase are a set of immediate-term recommendations for quick wins, a detailed roadmap outlining the path from the current state to the desired future state, and a series of workshops to ensure full stakeholder alignment.
Phase 2: Build
With a clear roadmap in place, the next phase focuses on building the necessary infrastructure to support the scaling plan. The goal of the Build phase is to develop the optimal team structure and to identify and onboard the required resources. This is where the customized staffing models are designed and implemented. We create hybrid integrations, such as a permanent core team designed to oversee a flexible group of fractional and embedded resources. We scale the business operations by building talent pipelines, implementing HR IT systems, and establishing the key performance metrics and dashboards that will be used to manage the new organization. We also support the build-out of training models and the development of the SOPs that will ensure process consistency. The deliverables from this phase include a detailed implementation plan with phased rollouts, customized tools such as staffing playbooks, and pilot programs to demonstrate the effectiveness of the new model and secure early victories.
Phase 3: Operate
Once the new model is built, the focus shifts to ongoing management and optimization. The goal of the Operate phase is to oversee the overall performance of the deployed teams and to support their continuous improvement. This is not a "set it and forget it" model. We use a data-driven approach to monitor and optimize the performance of the deployed staffing models, providing operational dashboards and reports that give leadership clear visibility into what is working and what is not. Based on this data and on fluctuating project demand, we recommend dynamic adjustments to the staffing models. We also ensure ongoing compliance and scalability through periodic audits and collaborative expansion planning. A critical component of this phase is knowledge management and transfer, ensuring that the expertise developed within the embedded and fractional teams is captured and becomes part of the SMO’s institutional knowledge. Key deliverables include the operational dashboards, comprehensive training programs and documentation, and scalable staffing contracts that provide on-demand access to curated pools of pre-vetted talent.
This iterative ABO process creates a powerful flywheel effect, allowing the SMO to continuously learn, adapt, and improve as it scales. It transforms the daunting task of growth into a manageable, de-risked, and repeatable process.
About the Strategic Solutions Group
This perspective is brought to you by the Strategic Solutions Group (SSG), the consulting and solutions arm of Barrington James. Barrington James is a global leader in life science recruitment, and SSG leverages this unparalleled network and deep industry expertise to bridge the critical gap between strategy and execution for pharmaceutical and life science innovators and their investors.
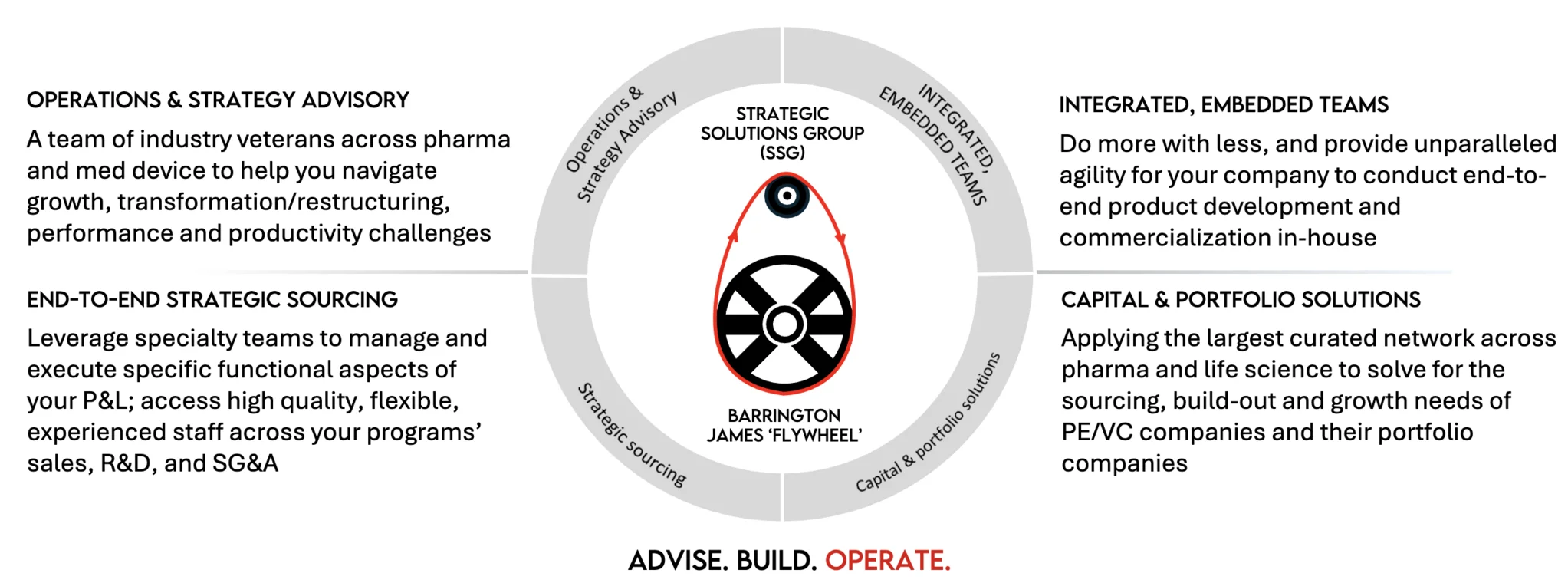
Our unique position within the Barrington James ecosystem allows us to offer a truly integrated suite of services. Our advisory services, staffed by a team of industry veterans from across the pharma and med-device sectors, deliver actionable roadmaps for efficiency and growth. These strategies are then brought to life through our flexible solutions, which include the deployment of integrated and embedded development and commercial teams, Functional Service Provider (FSP) models, and bespoke capital and portfolio solutions for private equity and venture capital clients.
This combination of "thinkers and doers" allows us to not only devise the optimal strategy but also to provide the expert operational horsepower required to de-risk and accelerate our clients' programs and investments. Our Advise-Build-Operate model is the mechanism through which we deliver this value, providing a structured, end-to-end partnership that drives tangible results. Whether navigating growth, transformation, and performance improvement, SSG provides the insights and resources critical to win in a competitive market.
Get in Touch
To explore how Barrington James Strategic Solutions Group can become a trusted partner in your organization’s long-term success, connect directly with our leadership.
Contact:

Bryan Katz
President, Barrington James Strategic Solutions Group
bkatz@barringtonssg.com